Advanced Imaging with Multiphoton and Nonlinear Techniques
Non-linear optics plays a crucial role in the microscopy of living organisms, enabling biological structures to be explored with greater precision and depth. Unlike linear optics, where the material's response is proportional to light intensity, non-linear optics involves complex phenomena.
In microscopy, this translates into the use of specific light interactions, such as second harmonic generation (SHG), third harmonic generation (THG), and multiphoton excitation microscopy.
Spontaneous activity of cortical neurons in brain mice slices at P6 illustrated by calcium imaging (R. Cossart team)
applications
These techniques are particularly advantageous for observing living biological tissues as they allow deep imaging.
Multiphoton microscopy, for instance, uses infrared laser pulses that penetrate deep into tissues (up to 1 mm) while causing less phototoxic damage, thus better preserving living biological structures. Additionally, it generates fluorescence signals only at the focal point, offering high-resolution three-dimensional imaging.
At PICsL, we develop innovative approaches for both in vitro and in vivo models.
Recently, we have extended the classical two-photon approach with a setup enabling three-photon excitation at the INMED facility, offering advantages such as enhanced safety, deeper imaging, and improved signal-to-noise ratio.
Non-labeled imaging techniques, such as second and third harmonic generation, are particularly useful for visualizing structures like collagen fibers or for revealing interfaces between different media, such as cell membranes and the cytoplasm.
Available Systems :
At IBDM:
- LSM 880 NLO with AiryScan: A versatile system for in-depth imaging (< 400 µm) in living samples. It enhances resolution in two-photon microscopy and provides a wide range of spectral combinations, including SHG capabilities.
- LSM 510 NLO: Equipped with new GaAsP detectors, this system enables simultaneous acquisition in two colors for streamlined and efficient experiments.
At INMED:
- TriMscope (Multibeam, Multiphoton Microscope): Scans samples with 64 beamlets, significantly increasing acquisition speed (over 10 Hz for a full field of 400 x 400 µm). This system is dedicated to dynamic calcium imaging in brain slices.
- CircuitPhotonics Facility:
- A 2&3 photon microscope for deep live imaging.
- A 2-photon endoscope for recording neuronal activity in freely moving mice during behavioral experiments.
- An AODscope (Acousto-Optic Deflector-based microscope), which allows live optical recording of cell membrane voltage and decoding of individual neuronal spikes.
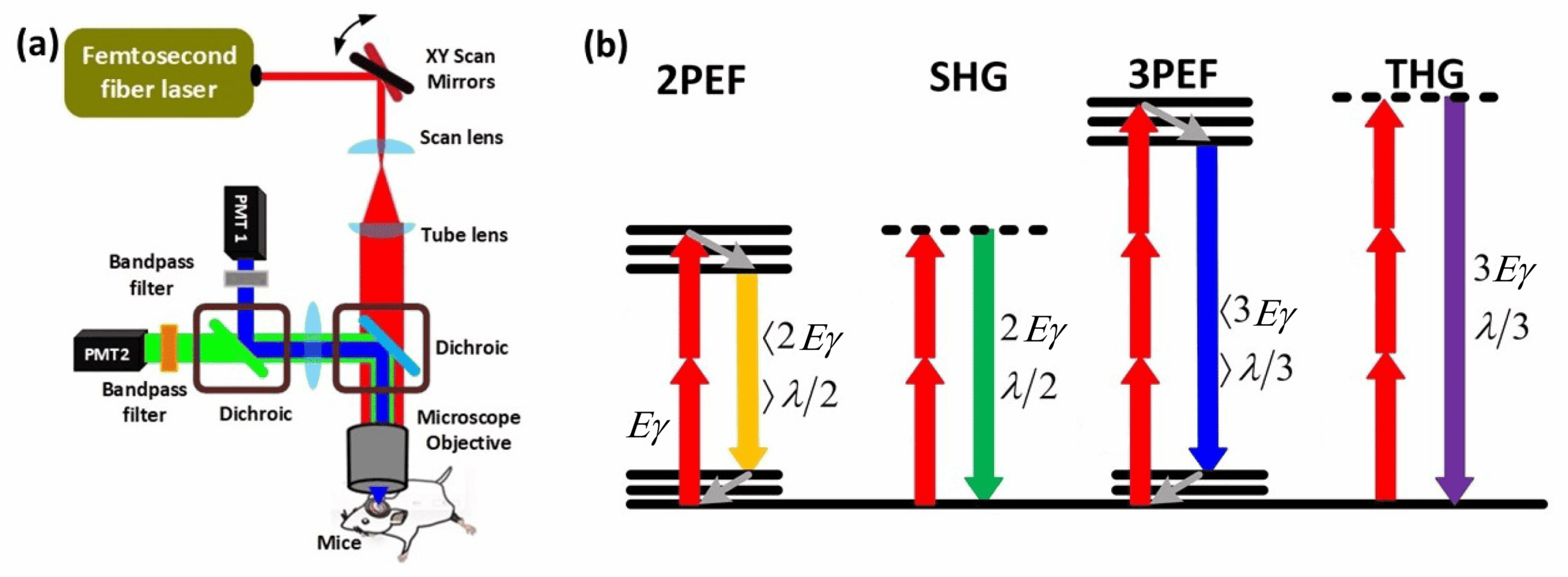

Deep imaging with multiphoton and harmonic generation techniques.

Three-photon microscopy for deeper imaging and better resolution.

Non-labeled imaging reveals structures like collagen and cell interfaces.

Cutting-edge systems for live and dynamic biological imaging.

Supports advanced neuronal activity and calcium dynamics studies.